Understanding Structural Steel Construction
Definition and Key Benefits
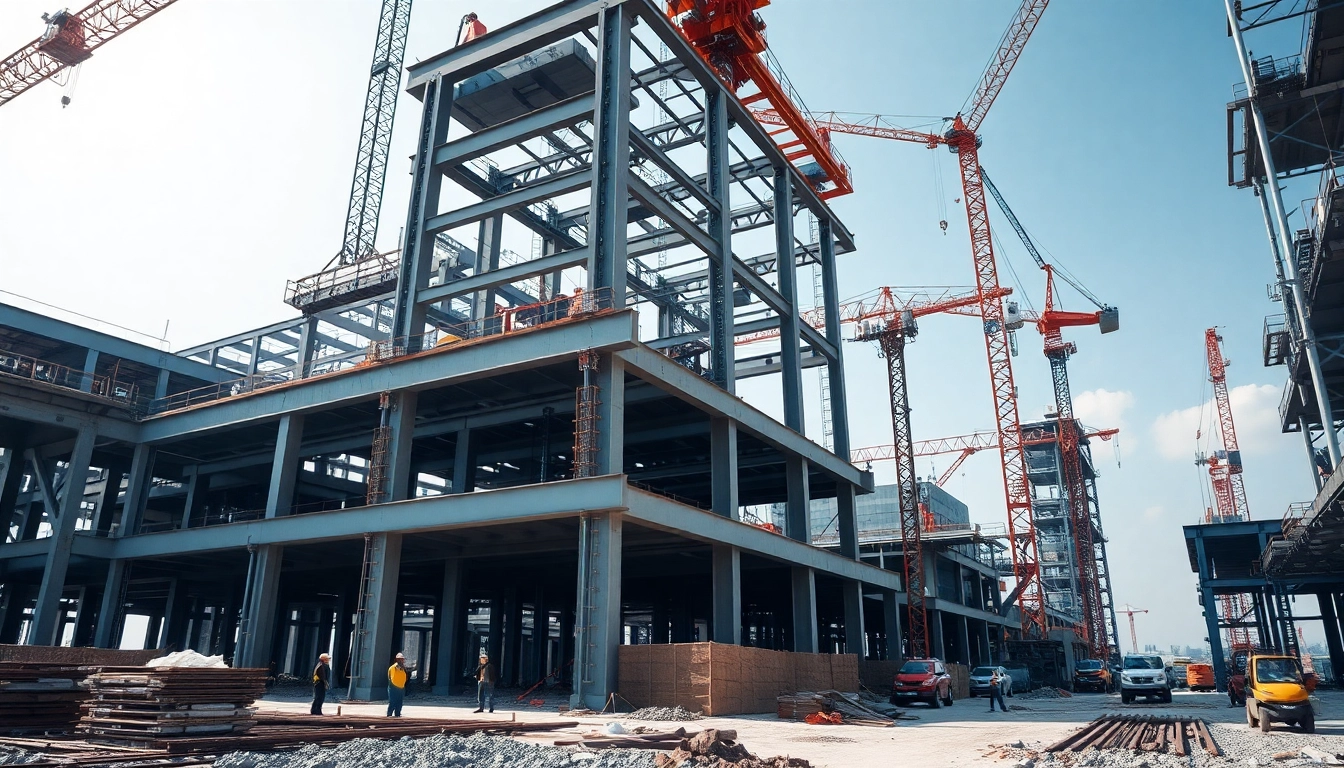
Structural steel construction involves utilizing steel sections to create frameworks for buildings and other structures. Known for its strength, versatility, and durability, structural steel is a preferred material in modern construction. The key benefits of using structural steel include:
- High Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Structural steel can support large loads while being relatively lightweight, allowing for taller and more complex designs.
- Design Flexibility: With various shapes, sizes, and grades available, structural steel can be adapted to meet the specific needs of a project.
- Speed of Construction: Pre-fabricated steel components can be quickly assembled on-site, leading to reduced construction time.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Although the initial material cost can be high, the long-term durability and low maintenance costs often result in overall savings.
- Sustainability: Steel is recyclable, making it a sustainable choice for construction projects.
For these reasons, structural steel construction has become a staple in building infrastructures worldwide.
Types of Structural Steel Used
Various types of structural steel are utilized in construction projects. Here, we will explore some of the most common types:
- Hot-Rolled Steel: This form of steel is created by rolling the steel at high temperatures, which makes it malleable. Hot-rolled steel is primarily used for beams, columns, and framing.
- Cold-Rolled Steel: Unlike hot-rolled steel, cold-rolled steel is processed at room temperature, leading to better surface finishes and tighter tolerances. It is often used for lighter structures.
- Steel Plates: Flat plates are used in a variety of applications, including as the base for columns or as braces in different types of constructions.
- Steel Beams: Available in various shapes, such as I-beams, H-beams, and channel beams, these components form the backbone of most structural steel systems.
- Structural Tubing: Hollow tubes with equal or unequal thickness provide strength without excessive weight, making them ideal for a variety of applications.
Common Applications in Construction
Structural steel is ubiquitous in construction due to its versatility. Here are some common applications:
- Commercial Buildings: Structural steel is often utilized in skyscrapers, office buildings, and shopping centers due to its ability to support large spans.
- Industrial Structures: Factories, warehouses, and other industrial facilities often rely on structural steel due to its strength and ability to support heavy machinery.
- Bridges: The high tensile strength of structural steel makes it ideal for bridge construction, allowing for long spans without needing intermediate supports.
- Residential Projects: Steel framing is becoming more popular in residential construction for its durability and flexibility in modern designs.
- Infrastructure Projects: Highways, railways, and airport terminals frequently employ structural steel for its robustness and efficiency.
Design Principles for Structural Steel Construction
Load-Bearing Considerations
When designing a structural steel framework, understanding load-bearing principles is paramount. This involves recognizing the types of loads that the structure will face, including:
- Dead Loads: These are static forces such as the weight of the structure itself, materials, and fixtures.
- Live Loads: These are dynamic forces caused by occupancy, furniture, and other movable elements.
- Environmental Loads: Wind, snow, and seismic activity can impose significant stress on buildings and must be accounted for during design.
Designers must ensure that all structural elements can safely support the anticipated loads, employing safety factors to account for unforeseen stresses.
Architectural and Aesthetic Choices
Structural steel also allows for unique architectural designs that blend functionality with aesthetics. Key considerations include:
- Form and Shape: The inherent flexibility of steel enables architects to create unconventional designs and shapes.
- Surface Treatments: Techniques such as powder coating and galvanization enhance the appearance and corrosion resistance of steel.
- Integration with Other Materials: Combining steel with concrete, glass, or wood can produce striking aesthetics, blending different characteristics.
Safety Standards and Compliance
Safety is crucial in structural steel construction. Adherence to local regulations and international standards, such as the American Institute of Steel Construction (AISC) guidelines, is essential to ensure the safety and stability of buildings. Common standards include:
- Structural Integrity: The design must withstand expected loads while ensuring safety against factors like corrosion and fatigue.
- Fire Resistance: Structural elements often need fireproofing measures to meet code requirements.
- Quality Assurance: Regular inspections and certifications during manufacture and construction ensure compliance with specifications.
Planning a Structural Steel Construction Project
Initial Site Assessments and Surveys
Before diving into a structural steel construction project, conducting thorough site assessments is essential. This includes:
- Soil Testing: Understanding the soil type and conditions ensures the foundation will adequately support the structure.
- Environmental Impact Assessments: Evaluating potential impacts on the surrounding environment helps in obtaining necessary permits.
- Utility Mapping: Identifying existing utilities such as water, gas, and electricity is crucial to avoid disruptions during construction.
Budgeting for Steel Materials
Creating an accurate budget for a structural steel project involves understanding the costs associated with:
- Material Costs: Prices can fluctuate based on market conditions, and sourcing from different suppliers may impact cost-effectiveness.
- Fabrication Costs: Costs associated with cutting, welding, and preparing steel elements for assembly can add to the budget.
- Labor Costs: Skilled labor for installation and other tasks must be factored into the overall budget.
Regularly reviewing and adjusting the budget throughout the project can help manage costs effectively.
Workflow and Timeline Management
Organizing the workflow and timeline of a construction project is crucial for efficiency. Considerations include:
- Project Scheduling: Establishing milestones and deadlines helps to keep the project on track and within budget.
- Coordination among Trades: Ensuring seamless collaboration between various contractors (e.g., electricians, plumbers) is essential for avoiding conflicts.
- Regular Progress Monitoring: Keeping track of progress can identify delays and allow for immediate adjustments to workflows.
Best Practices in Structural Steel Construction
Efficient Fabrication Techniques
Efficiency in fabrication contributes to cost savings and improved timelines. Best practices include:
- Advanced Cutting Methods: Utilizing laser and water jet cutting can increase precision and reduce waste.
- Pre-Fabrication: Off-site fabrication of elements allows for concurrent site work and assembly, reducing delays.
- Lean Manufacturing Principles: Implementing lean practices reduces waste and focuses on producing only what is needed when it is needed.
On-Site Assembly and Quality Control
The on-site assembly phase is critical in ensuring the integrity of the structural steel framework. Key practices include:
- Pre-Assembly Coordination: Ensuring all parts are available and workers are trained before assembly begins.
- Regular Inspections: Conducting quality checks at different stages of assembly to ensure everything meets design specifications.
- Utilizing Technology: Employing tools like 3D modeling and structural analysis software to simulate the assembly before actual on-site work.
Utilizing Technology in Construction
Technology plays a pivotal role in modern structural steel construction. Advancement in technology has led to improved efficiency and effectiveness in various phases of construction, including:
- BIM (Building Information Modeling): This digital representation assists in planning, designing, and managing construction projects more effectively.
- 3D Scanning: Accurate site measurements and conditions can be recorded, allowing for comprehensive planning and adjustments during construction.
- Project Management Software: Tools that assist in tracking progress and managing project schedules can enhance communication among all project stakeholders.
Future Trends in Structural Steel Construction
Innovative Materials and Techniques
The landscape of structural steel construction is evolving with innovative materials and techniques. Key advancements include:
- High-Strength Steel: Emerging alloys provide higher strengths, allowing for lighter structures that maintain or enhance load-bearing capacity.
- Smart Steel: Incorporating sensors and technologies in steel structures can provide real-time data on stress, temperature, and energy usage.
- 3D Printing: This technology is beginning to influence the production of customized steel components tailored for specific projects.
Sustainability Considerations
Sustainability is an increasingly vital aspect of modern construction. Considerations in structural steel construction include:
- Recyclable Materials: Steel is one of the most recycled materials globally, minimizing waste and promoting sustainability.
- Efficient Resource Use: Strategies to reduce energy consumption during fabrication and installation contribute to a more sustainable construction process.
- Green Building Certifications: Buildings striving for certifications like LEED incorporate sustainable practices and materials.
The Role of Automation and Robotics
Automation and robotics are revolutionizing the construction industry, especially in structural steel construction. This includes:
- Automated Welding: Enhancing precision and reducing human error, automated welding systems improve the quality of connections.
- Robotic Assembly: Robots equipped with advanced sensors can assist in the on-site assembly of steel components, increasing efficiency.
- Drones for Monitoring: Drones are increasingly being utilized for site surveys and monitoring progress, offering valuable insights into project health.